Why should work ability be managed strategically?
Strategic work ability management means making good work ability a strategic goal of the organisation. It is systematic actions that integrate work ability management into the organisation’s management system and day-to-day supervisory work.
When the resilience and well-being of employees are carefully planned and managed as part of the entire workplace’s activities, it benefits both the employees and the workplace. Employees enjoy greater well-being, and the workplace is more efficient. Impactful work ability management is not just random actions – it is based on clear structures and operating models that everyone is familiar with and uses.
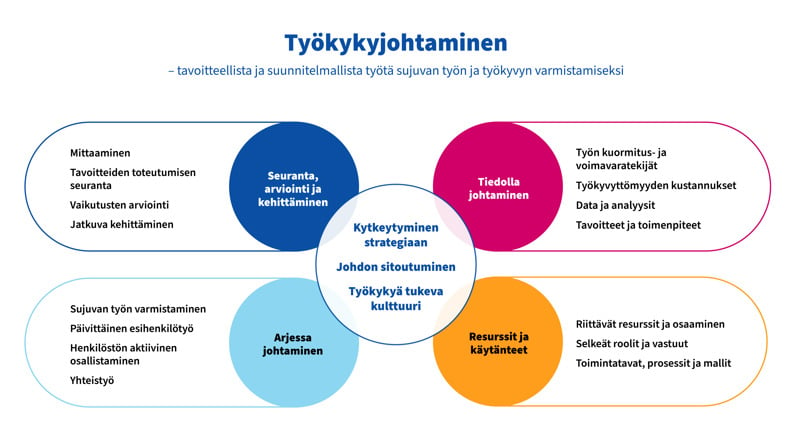
Elements of strategic work ability management
The starting point for strategic work ability management is a culture that supports work ability and which actively involves the employees in developing work ability management. When the employees participate in planning and assessing, the work ability culture is strengthened.
It is thus not just about single measures but about daily activities that are linked to the company’s strategy and goals.
Management is in a key position in creating this culture. It must be committed to ensuring work ability and understand how work ability affects the success of the entire organisation.